Before Vasectomy: The vas deferens serves as the conduit for transporting sperm from the epididymis in preparation for ejaculation. Situated on the posterior surface of the testis, the epididymis stores and matures sperm. Two ducts connect the left and right epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts to facilitate sperm movement. Each tube measures approximately 30 centimeters in length. During ejaculation, the smooth muscles in the walls of the vas deferens contract reflexively, propelling sperm forward. These sperm are then transferred from the vas deferens into the urethra, mingling with secretions from male accessory sex glands—such as the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands—which collectively form semen.
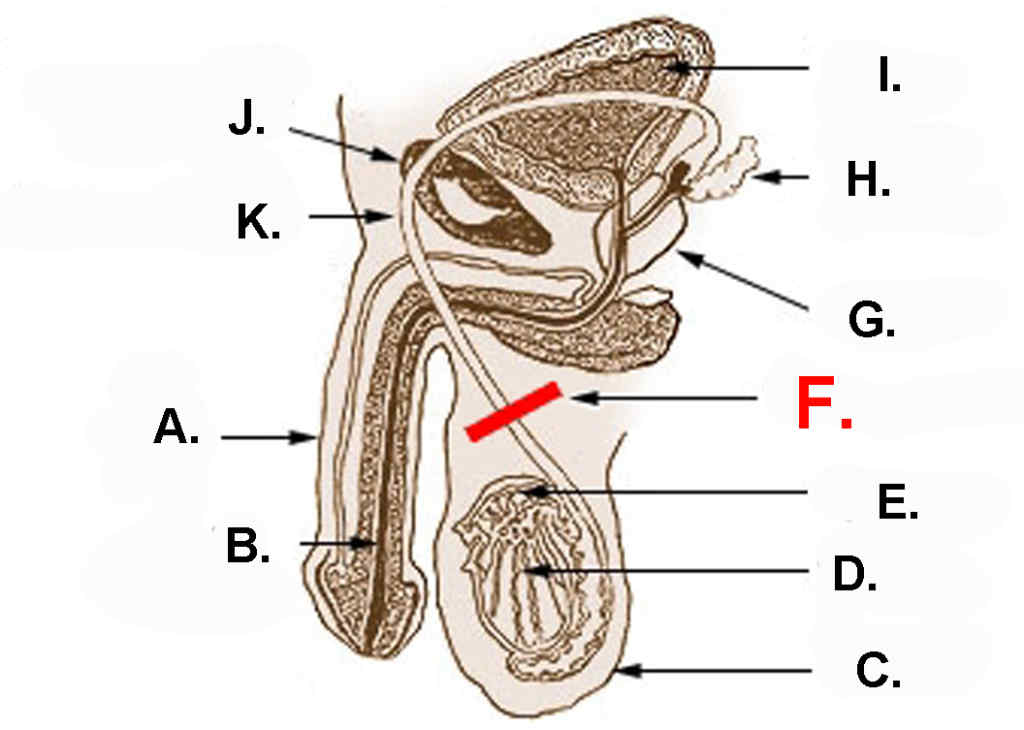
Diagram showing the usual location of a vasectomy:
| A.) Penis | B.) Urethra | C.) Scrotum |
| D.) Testicle | E.) Epididymis | F.) Vasectomy |
| G.) Prostate | H.) Seminal vesicle | I.) Bladder |
| J.) Pubic bone | K.) Vas deferens |
During the Vasectomy: A vasectomy is a method of contraception or male sterilization that involves permanently cutting the vasa deferentia (plural for vas deferens). In this procedure, the vasa deferentia are severed and sealed to prevent sperm from entering the seminal stream (ejaculate). Our approach to vasectomy involves using a sharp hemostat to puncture the scrotum and then severing and sealing the vasa deferentia, a technique known as a no-scalpel vasectomy.
After Vasectomy: Post-vasectomy, the connection between the testes and the penis via the tube is severed. However, the testes remain active and functional; Leydig cells continue producing testosterone and hormones, which are absorbed into the bloodstream. Although sperm are still produced by the testes, their path is interrupted. Produced sperm are broken down by the body, with the epididymis’s membranes absorbing the resulting liquid, while solid substances are metabolized by macrophages and absorbed into the bloodstream. The epididymis’s membranes may enlarge to accommodate increased liquid absorption due to the accumulation of stagnant sperm. Additionally, the immune system may increase the number of macrophages to manage the elevated solid waste.
Post-vasectomy observations include:These factors collectively contribute to the understanding that while a vasectomy interrupts the path of sperm, it does not affect other aspects of male sexual function or reproductive health.
Note: One Stop Medical Center provides the service of no-Scalpel Easy Vasectomy. We have two office locations in Edina, Minnesota, and Casselberry, Florida. If you are interested in vasectomy, Please fill out the online registration first, we will call you in 2 business days, or please call us at 1-888-992-0019 if any questions.




